Nissan Rogue Service Manual: Cylinder block
Exploded View
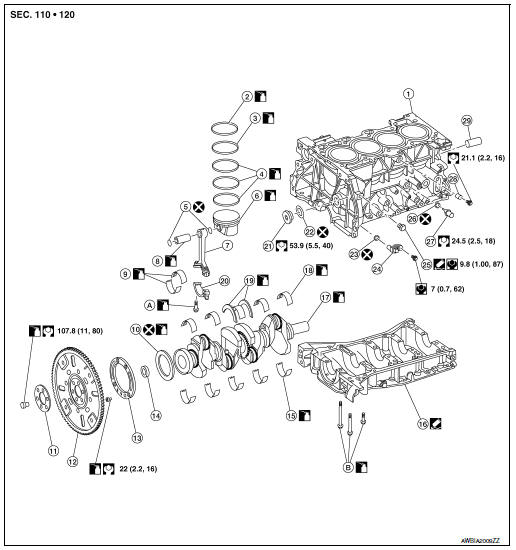
- Cylinder block
- Top ring
- Second ring
- Oil ring
- Snap ring
- Piston
- Connecting rod
- Piston pin
- Connecting rod bearing
- Rear oil seal
- Reinforcement plate
- Drive plate
- Signal plate
- Pilot converter
- Main bearing (lower)
- Lower cylinder block
- Crankshaft
- Main bearing (upper)
- Thrust bearing
- Connecting rod bearing cap
- Drain plug
- O ring
- O ring
- Crankshaft position sensor
- . Drain plug
- O ring
- Oil temperature sensor
- . Knock sensor
- Cylinder block heater (if equipped)
- Refer to INSTALLATION
- Refer to INSTALLATION
Disassembly and Assembly
DISASSEMBLY
- Mount the engine on a suitable engine stand. Refer to EM-91, "Setting".
- Drain any remaining engine oil and engine coolant, (if necessary).
- Remove drain plugs from cylinder block.
- Remove cylinder block heater (if equipped).
- Remove cylinder head. Refer to EM-54, "Exploded View".
- Remove knock sensor.
CAUTION: Carefully handle knock sensor avoiding shocks.
- Remove crankshaft position sensor (POS) (2).
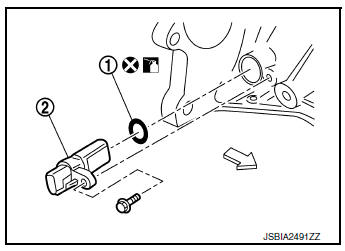
(1) : O-ring
 : Engine front
: Engine front
CAUTION:
- Avoid impacts such as dropping.
- Do not disassemble.
- Keep crankshaft position sensor (POS) away from metal particles.
- Do not place crankshaft position sensor (POS) in a location where it is exposed to magnetism.
- Remove oil temperature sensor.
CAUTION: Do not reuse O-ring.
- Remove piston and connecting rod assembly with the following procedure:
- Before removing piston and connecting rod assembly, check the connecting rod side clearance. Refer to EM-100, "Inspection".
- Position crankshaft pin corresponding to connecting rod to be removed onto the bottom dead center.
- Remove connecting rod cap. Number connecting rod caps so they can be assembled in the same position and direction.
- Using a hammer handle or similar tool, push piston and connecting rod assembly out to cylinder head side.
CAUTION:
- Do not damage matching surface with connecting rod cap.
- Do not damage cylinder wall and crankshaft pin, resulting from an interference of the connecting rod big end.
NOTE: Number the pistons and rods so they can be installed in the same position.
- Remove connecting rod bearings.
CAUTION: When removing them note the installation position. Keep them in the correct order.
- Remove piston rings from piston.
- Before removing piston rings check the piston ring side clearance. Refer to EM-100, "Inspection".
- Remove piston rings using suitable tool (A).
CAUTION:
- When removing piston rings, be careful not to damage the piston.
- Do not damage piston rings by expanding them excessively.
- Remove piston from connecting rod using the following procedure:
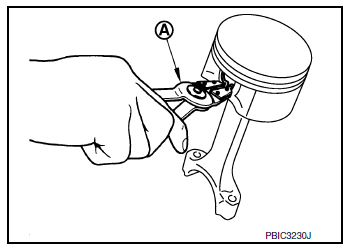
- Remove snap rings using snap ring pliers (A).
- Heat piston to 60°C to 70°C (140°F to 158°F) with a heat gun (A).
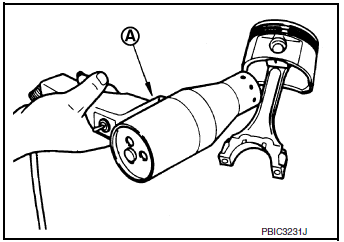
- Push out piston pin using a suitable tool.
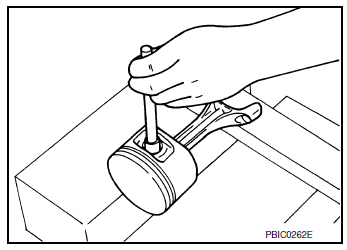
- Remove lower cylinder block using the following procedure:
- Measure crankshaft end play before loosening lower cylinder block bolts. Refer to EM-100, "Inspection".
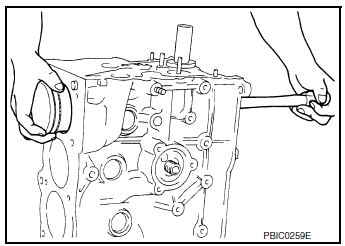
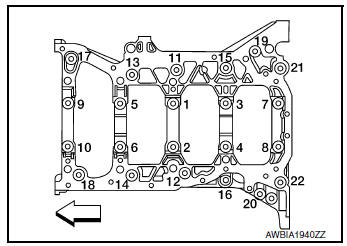
- Loosen and remove lower cylinder block bolts in reverse order as shown.
- Remove the lower cylinder block using Tool (A).
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage the mating surfaces.
NOTE: In areas where the cutter is difficult to use, use a plastic hammer to lightly tap (1) the cutter where the liquid gasket is applied. Use a plastic hammer to slide (2) the cutter by tapping on the side.
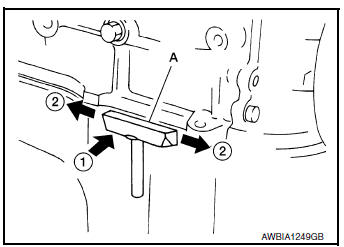
Tool number : KV10111100 (J-37228)
- Remove the lower cylinder block while tapping lightly with a plastic hammer.
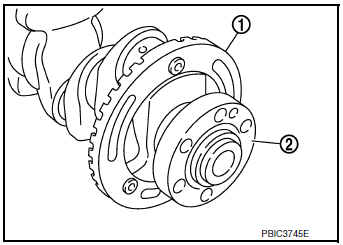
- Remove crankshaft (2).
CAUTION:
- Do not damage or deform signal plate (1) mounted on crankshaft.
- When setting crankshaft on a flat floor surface, use a block of wood to avoid contact between signal plate and floor surface.
- Do not remove signal plate unless it is necessary.
- Remove rear oil seal from rear end of crankshaft.
CAUTION: Do not damage the crankshaft or cylinder block when removing the rear main seal.
- Remove main bearing (upper and lower) and thrust bearings from
cylinder block and lower cylinder block.
CAUTION: When removing bearings note the installation position. Keep them in the correct order.
NOTE: When removing the rear oil seal without removing the cylinder block, use a suitable tool to pull it out between the crankshaft and block.
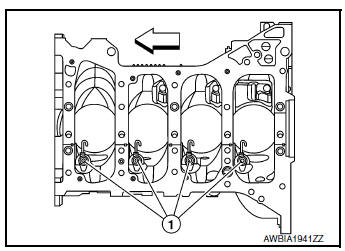
- Remove oil jets (1) from cylinder block.
CAUTION: When removing oil jet assemblies note the installation position.
Keep them in the correct order.
ASSEMBLY
- Fully air-blow engine coolant and engine oil passages in cylinder block,
cylinder bore and crankcase to
remove any foreign material.
CAUTION: Use goggles to protect your eyes.
- Install drain plugs to cylinder block as shown.
CAUTION: Do not reuse washer (1).
- Apply liquid gasket to the threads of drain plug (3).
Use Genuine RTV Silicone Sealant or equivalent. Refer to GI-22, "Recommended Chemical Products and Sealants".
NOTE: Do not apply liquid gasket to the thread of plug (2).
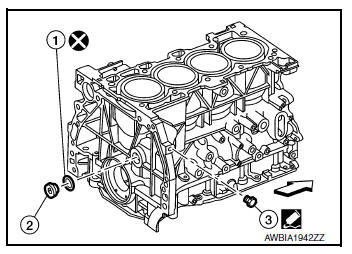
- Tighten each plug as specified below.
- Install oil jets (1).
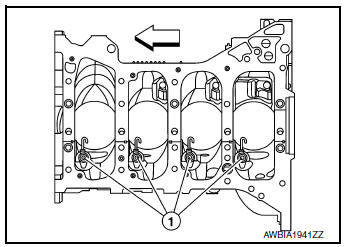
Oil jets (1) : 23 N·m (2.3 kg-m, 17 ft-lb)
- Install main bearings and thrust bearings using following procedure:
- Remove dust, dirt, and engine oil on the bearing mating surfaces of cylinder block and lower cylinder block.
- Install thrust bearings (1) to both sides of the No. 3 journal (A) housing on cylinder block.
- Install thrust bearings with the oil groove (B) facing crankshaft arm (outside).
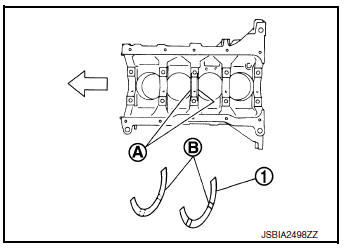
- Install the main bearings paying attention to the direction.
- Main bearing with an oil hole and groove (E) goes on cylinder block. The one without them (C) goes on lower cylinder block.
- Only main bearing (on cylinder block) for No. 3 journal (2) has different specifications.
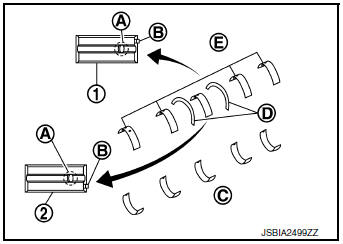
(1) : Journal other than no. 3
(D) : Thrust bearings
- Before installing main bearings, apply new engine oil to the bearing surface (inside). Do not apply engine oil to the back surface, but thoroughly clean it.
- When installing, align main bearing stopper (B) to the notch.
- Ensure the oil holes (A) on cylinder block and those on the corresponding bearing are aligned.
- Install signal plate to crankshaft (if removed).
- Set the signal plate with flange facing toward the counterweight side (engine front side).
- After positioning crankshaft (2) and signal plate (1) with positioning dowl pin (A), tighten bolts.
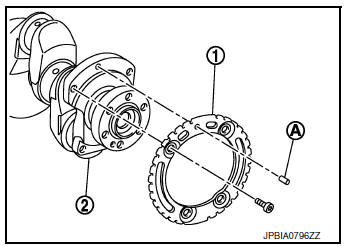
(1) : Signal plate
(2) : Crankshaft
(A) : Dowel pin (used to position the signal plate)
- Remove dowel pin.
CAUTION: Be sure to remove dowel pin.
- Install crankshaft to cylinder block.
- While turning crankshaft by hand, check that it turns smoothly.
CAUTION: Do not install rear oil seal yet.
- Install lower cylinder block with the following procedure:
- Apply liquid gasket with a suitable tool to lower cylinder block.
Use Genuine RTV Silicone Sealant or equivalent. Refer to GI-22, "Recommended Chemical Products and Sealants".
(B) : Apply liquid gasket to an end
(a) : 4.0 - 5.0 mm (0.157- 0.197 in)
NOTE: Lower cylinder block cannot be replaced as a single part because it is machined together with cylinder block.
- Apply new engine oil to threads and seat surfaces of the bolts.
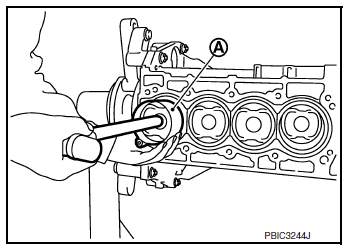
- Tighten lower cylinder block bolts to specification in the numerical order as shown.
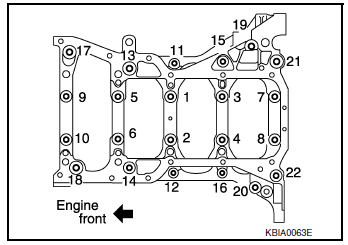
- Tighten bolts to specification using suitable tool and Tool (A).
CAUTION: Check tightening angle. Do not judge angle by visual inspection.
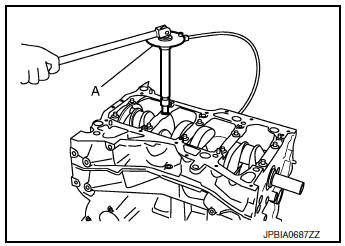
Step 1, bolts 11 - 22 only : 25.1 N·m (2.6 kg-m, 19 ft-lb)
Step 2, bolts 1 - 10 only : 39.2 N·m (4.0 kg-m, 29 ft-lb)
Step 3, bolts 1 - 10 only : 60°degrees rotation
Tool number (A) : KV10112100 (BT-8653-A)
- Install rear oil seal. Refer to EM-79, "REAR OIL SEAL : Removal and Installation".
- After installing bolts, check that crankshaft can be rotated smoothly by hand.
- Wipe off completely any protruding liquid gasket on front side of engine.
- Check crankshaft end play. Refer to EM-100, "Inspection".
- Install piston to connecting rod with the following procedure:
- Install new snap ring to the groove of the piston rear side using snap ring pliers.
- Insert it fully into groove to install.
CAUTION: Do not reuse snap rings.
- Assemble piston to connecting rod.
- Using a heat gun, heat piston until piston pin can be pushed in by hand without excess force [approximately 60°C to 70°C (140°F to 158°F)]. From the front to the rear, insert piston pin into piston and connecting rod.
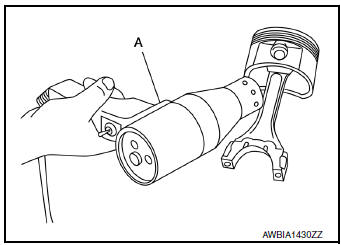
- Set so that the front mark (A) on the piston head, the oil splash (B) and the cylinder number (C) on connecting rod are positioned as shown.
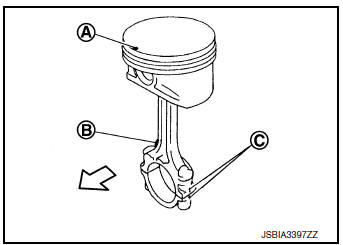
- Install new snap ring to the groove of the piston front side.
- Insert it fully into groove to install.
- After installing, check that connecting rod moves smoothly.
- Install piston rings using suitable tool.
- Position each ring with the gap as shown referring to the piston front mark (B).
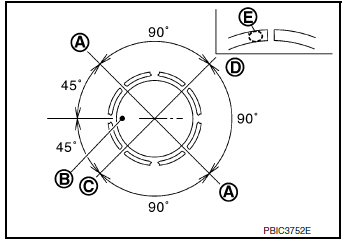
(A) : Oil ring upper or lower rail gap (either of them)
(C) : Second ring and oil ring spacer gap
(D) : Top ring gap
- Install second ring with the stamped surface (E) facing upward.
CAUTION:
- Do not damage piston.
- Do not damage piston rings by expanding them excessively.
- Do not contact rail end gap under oil ring with oil drain cast groove of piston.
- Install connecting rod bearings to connecting rod and connecting rod cap.
- When installing connecting rod bearings apply new engine oil to the bearing surface (inside). Do not apply engine oil to the back surface, but thoroughly clean it.
- When installing, align the connecting rod bearing stopper protrusion (A) with the cutout (B) of connecting rod and connecting rod cap to install.
- Ensure the oil hole on connecting rod and that on the corresponding bearing are aligned.
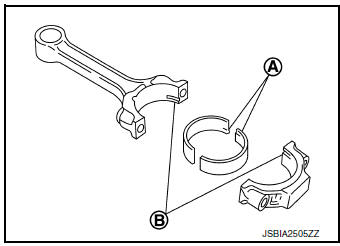
- Install piston and connecting rod assembly to crankshaft.
- Position crankshaft pin corresponding to connecting rod to be installed onto the bottom dead center.
- Apply new engine oil sufficiently to the cylinder bore, piston and crankshaft pin.
- Match the cylinder position with the cylinder number on connecting rod to install.
- Using a suitable tool, install piston with the front mark on the
piston head facing the front of the engine.
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage the cylinder wall and crankshaft pin, resulting from an interference of the connecting rod big end.
- Install connecting rod cap.
- Match the stamped cylinder number marks on connecting rod with those on connecting rod cap to install.
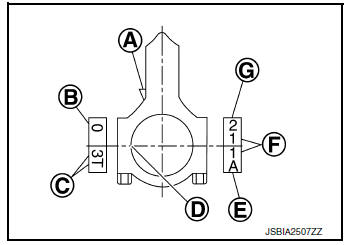
(A) : Oil splash
(B) : Small end diameter grade
(C) : Production control number
(D) : Bearing stopper groove
(E) : Production control number
(F) : Cylinder number
(G) : Big end diameter grade
- Tighten connecting rod bolt with the following procedure:
- Tighten the connecting rod bolts using Tool (A) as follows:
Apply engine oil to the threads and seats of the connecting rod
bolts.
CAUTION: Check tightening angle. Do not judge angle by visual inspection.
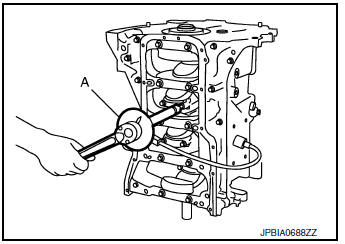
Step 1 : 27.4 N·m (2.8 kg-m, 20 ft-lb)
Step 2 : 0 N·m
Step 3 : 19.6 N·m (2.0 kg-m, 14 lb-ft)
Step 4 : Rotate bolts 90° + 0.5°
Tool number : KV10112100 (BT-8653-A)
- After tightening connecting rod bolts, check that crankshaft rotates smoothly.
- Check the connecting rod side clearance. Refer to EM-100, "Inspection".
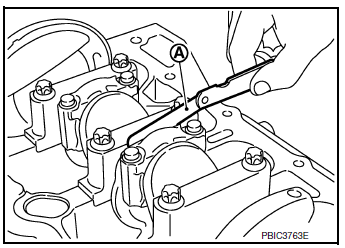
- Install knock sensor (1).
- Install knock sensor with connector facing 180° +/- 15° (a) as shown.
CAUTION:
- Do not tighten bolts while holding connector.
- If any impact by dropping is applied to knock sensor, replace it with a new one.
NOTE:
- Check that there is no foreign material on the cylinder block mating surface and the back surface of knock sensor.
- Check that knock sensor does not interfere with other parts.
- Install crankshaft position sensor (POS).
- Assembly of remaining components is in the reverse order of disassembly.
Inspection
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
- Measure clearance between thrust bearings and crankshaft arm when crankshaft is moved fully forward or backward using suitable tool (A).
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace thrust bearings and measure again. If it still exceeds limit replace crankshaft.
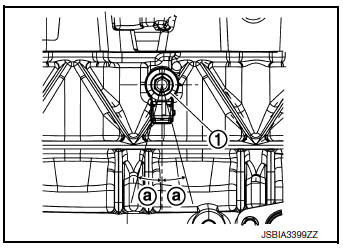
CONNECTING ROD SIDE CLEARANCE
- Measure side clearance between connecting rod and crankshaft arm using suitable tool (A).
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace connecting rod and measure again. If it still exceeds limit replace crankshaft.
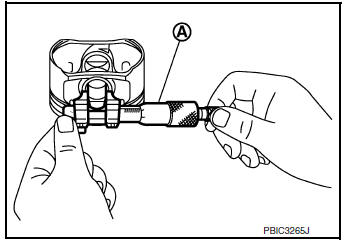
PISTON TO PISTON PIN OIL CLEARANCE
Piston Pin Hole Diameter
- Measure inner diameter of piston pin hole using suitable tool (A).
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Piston Pin Outer Diameter
- Measure outer diameter of piston pin using suitable tool (A).
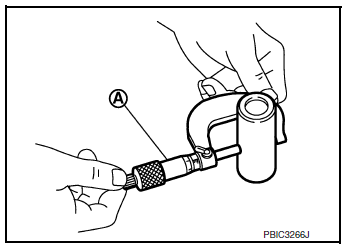
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Piston to Piston Pin Oil Clearance
- (Piston to piston pin oil clearance) = (Piston pin hole diameter) - (Piston pin outer diameter)
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If oil clearance value exceeds the limit replace piston and piston pin assembly.
NOTE: Piston is available together with piston pin as assembly.
PISTON RING SIDE CLEARANCE
- Measure side clearance of piston ring and piston ring groove using suitable tool (A).
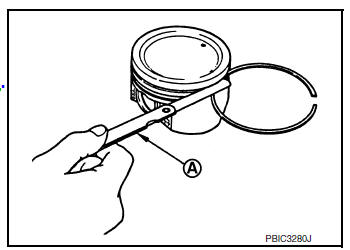
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace piston ring and measure again. If value still exceeds the limit replace piston.
CONNECTING ROD BEND AND TORSION
- Check with a connecting rod aligner.
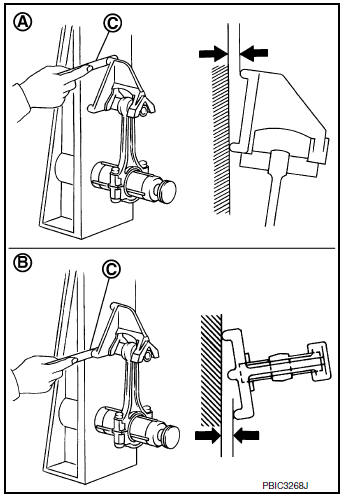
(A) : Bend
(B) : Torsion
(C) : Feeler gauge
Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace connecting rod assembly.
CONNECTING ROD BIG END DIAMETER
- Install connecting rod cap (1) without connecting rod bearing installed and tighten connecting rod bolts. Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
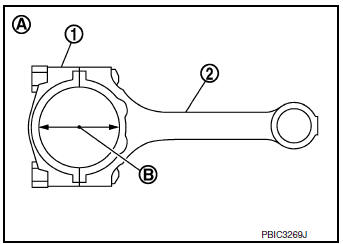
(2) : Connecting rod
(A) : Example
(B) : Measuring direction of inner diameter
- Measure inner diameter of connecting rod big end using suitable tool.
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds standard replace connecting rod assembly.
CONNECTING ROD BUSHING OIL CLEARANCE
Connecting Rod Bushing Inner Diameter
- Measure inner diameter of connecting rod bushing using suitable tool (A).
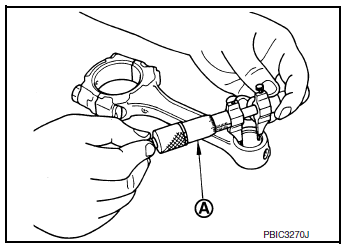
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Piston Pin Outer Diameter
- Measure outer diameter of piston pin using suitable tool (A).
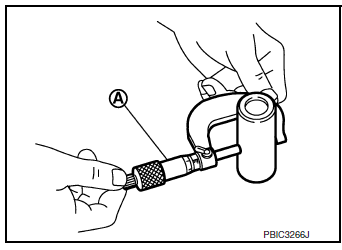
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Connecting Rod Bushing Oil Clearance
- (Connecting rod bushing oil clearance) = (Connecting rod bushing inner diameter) - (Piston pin outer diameter)
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds standard replace connecting rod assembly and/or piston and piston pin assembly.
CYLINDER BLOCK TOP SURFACE DISTORTION
- Remove gasket on the cylinder block surface and also remove engine
oil, scale, carbon and other contamination
using suitable tool.
CAUTION: Do not allow gasket flakes to enter engine oil or engine coolant passages.
- Measure distortion on cylinder block upper face at some different points in six directions using suitable tools (A/B).
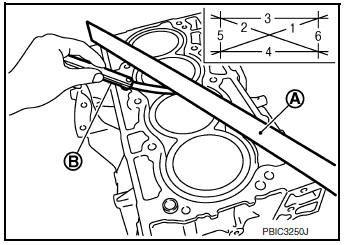
Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds standard replace cylinder block.
MAIN BEARING HOUSING INNER DIAMETER
- Install lower cylinder block without main bearings installed and tighten lower cylinder block bolts. Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
- Measure inner diameter of main bearing housing using suitable tool.
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds standard replace cylinder block (1) and
lower cylinder block (2) assembly.
NOTE: Lower cylinder block cannot be replaced as a single unit because it is machined together with cylinder block.
PISTON TO CYLINDER BORE CLEARANCE
Cylinder Bore Inner Diameter
- Measure cylinder bore for wear, out-of-round and taper at six different points on each cylinder using suitable tool. [(A) and (B) directions at (C), (D), and (E)] [(A) is in longitudinal direction of engine]
(f) : 10 mm (0.39 in)
(g) : 75 mm (2.95 in)
(h) : 140 mm (5.51 in)
NOTE: When determining cylinder bore grade, measure the cylinder bore at (B) position.
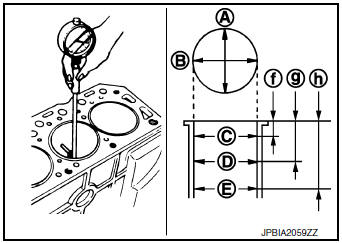
Standard:
Cylinder bore inner diameter
: Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Limit:
Out-of-round [Difference between (A) and (B)]
Taper [Difference between (C) and (D)]
: Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit or if there are scratches and/or seizure on the cylinder inner wall hone or rebore the cylinder inner wall.
Piston Skirt Diameter
- Measure outer diameter of piston skirt with suitable tool (A).
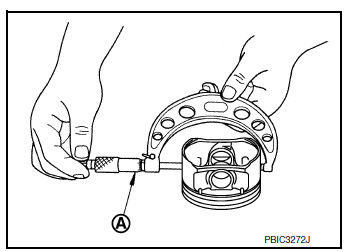
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
Piston to Cylinder Bore Clearance
- (Piston to cylinder bore clearance) = (Cylinder bore inner diameter) - (Piston skirt diameter)
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace piston and piston pin assembly..
PISTON RING END GAP
- Check that cylinder bore inner diameter is within standards.
- Lubricate with new engine oil to piston (1) and piston ring (2), and then insert (A) piston ring to middle of cylinder (B) with piston and measure piston ring end gap using suitable tool (C).
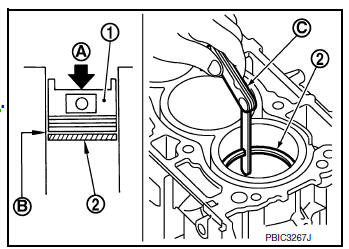
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace piston ring and measure again. If it still exceeds the limit replace cylinder block.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN JOURNAL DIAMETER
- Measure outer diameter of crankshaft main journals using suitable tool (A).
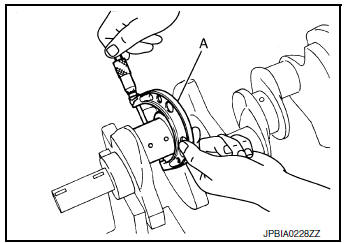
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit measure the main bearing oil clearance and use undersize bearing.
CRANKSHAFT PIN JOURNAL DIAMETER
- Measure outer diameter of crankshaft pin journal using suitable tool.
Standard : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit measure connecting rod bearing oil clearance and use undersize bearing.
OUT-OF-ROUND AND TAPER OF CRANKSHAFT
- Measure dimensions at four different points as shown on each main journal and pin journal using suitable tool.
- Out-of-round is indicated by the difference in dimension between (a) and (b) at (c) and (d).
- Taper is indicated by difference in dimension between (c) and (d) at (a) and (b).
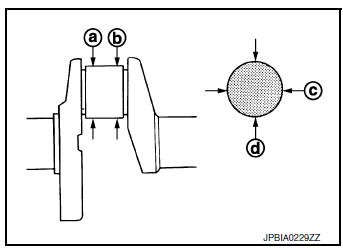
Limit: Out-of-round [Difference between (a) and (b)] Taper [Difference between (c) and (d)] : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit correct or replace crankshaft.
- If corrected, measure bearing oil clearance of corrected main journal and/or pin journal. Then select main bearing and/or connecting rod bearing.
CRANKSHAFT RUNOUT
- Place V-block on precise flat table to support the journals on both ends of crankshaft.
- Place suitable tool (A) straight up on No. 3 journal.
- While rotating crankshaft, read movement of pointer on suitable tool. (Total indicator reading)
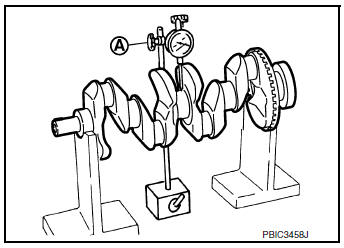
Limit : Refer to EM-120, "Cylinder Block".
- If measured value exceeds limit replace crankshaft.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING OIL CLEARANCE
Method by Calculation
- Install connecting rod bearings (2) to connecting rod (3) and connecting
rod bearings cap (1) and tighten connecting rod bolts.
Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
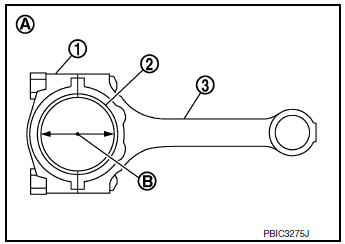
(A) : Example
- Measure inner diameter (B) of connecting rod bearing using suitable tool.
- (Bearing oil clearance) = (Connecting rod bearing inner diameter) - (Crankshaft pin journal diameter)
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-125, "Connecting Rod Bearing".
- If measured value exceeds limit select proper connecting rod bearing. Use connecting rod big end diameter and crankshaft pin journal diameter to obtain specified bearing oil clearance.
Method by Using Plastigage
- Remove engine oil and dust on crankshaft pin and the surfaces of each bearing completely.
- Cut plastigage slightly shorter than bearing width and place it in crankshaft axial direction avoiding oil holes.
- Install connecting rod bearings to connecting rod and cap and
tighten connecting rod bolts. Refer to EM-93,
"Disassembly and Assembly".
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft.
- Remove connecting rod cap and bearing and using the scale (A)
on the plastigage bag measure the plastigage width.
NOTE: The procedure when the measured value exceeds the limit is same as that described in the “Method by Calculation”
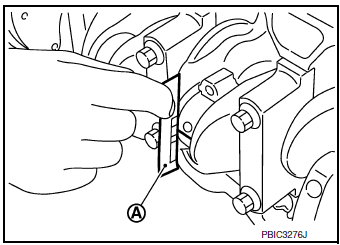
MAIN BEARING OIL CLEARANCE
Method by Calculation
- Install main bearings (3) to cylinder block (1) and lower cylinder block (2) and tighten lower cylinder block bolts. Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
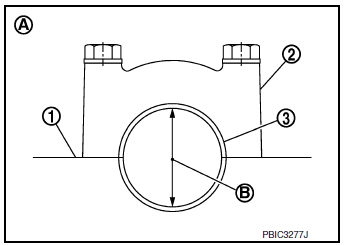
(A) : Example
- Measure the inner diameter (B) of main bearing with bore gauge.
- (Bearing oil clearance) = (Main bearing inner diameter) - (Crankshaft main journal diameter)
Standard and Limit : Refer to EM-123, "Main Bearing".
- If measured value exceeds limit select proper main bearing. Use
main bearing inner diameter and crankshaft main journal diameter to obtain
specified bearing oil clearance.
Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
Method by Using Plastigage
- Remove engine oil and dust on crankshaft main journal and surfaces of each bearing completely.
- Cut plastigage slightly shorter than bearing width and place it in crankshaft axial direction avoiding oil holes.
- Install main bearings on cylinder block and lower cylinder block
and tighten lower cylinder block bolts. Refer
to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft.
- Remove lower cylinder block and bearings and using the scale (A)
on the plastigage bag measure the plastigage width.
NOTE: The procedure when measured value exceeds the limit is same as that described in “Method by Calculation”.
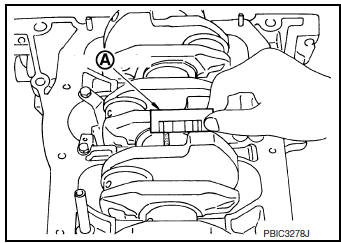
MAIN BEARING CRUSH HEIGHT
- When lower cylinder block is removed after being tightened to specified torque with main bearings (1) installed, tip end of bearing must protrude (B). Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
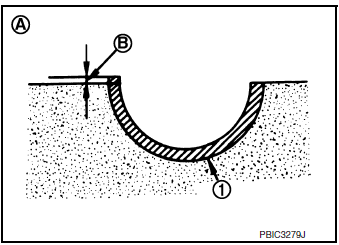
(A) : Example
Standard: There must be crush height.
- If standard is not met, replace main bearings.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CRUSH HEIGHT
- When connecting rod bearing cap is removed after being tightened to specified torque with connecting rod bearings (1) installed, tip end of bearing must protrude (B). Refer to EM-93, "Disassembly and Assembly".
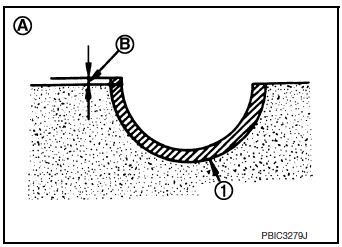
(A) : Example
Standard: There must be crush height.
- If standard is not met, replace connecting rod bearings.
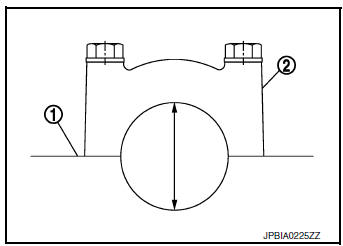
LOWER CYLINDER BLOCK BOLT OUTER DIAMETER
- Measure outer diameters (d1) and (d2) at two positions as shown.
- If reduction appears in (B) range, regard it as (d2).
Limit [(d1) - (d2)]: 0.13 mm (0.0051 in)
- If measured value exceeds limit (a large difference in dimensions) replace lower cylinder block bolt with new one.
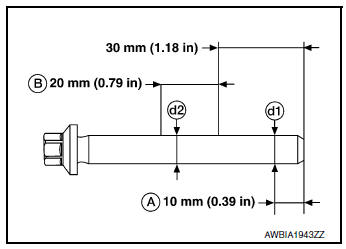
CONNECTING ROD BOLT OUTER DIAMETER
- Measure outer diameter (d) at position as shown.
- If reduction appears in position other than (d), regard it as (d).
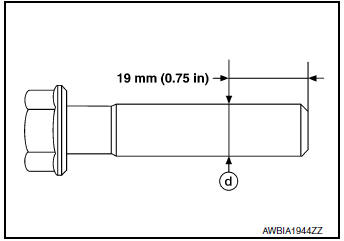
Limit: 7.75 mm (0.3051 in)
- If measured value exceeds limit (large difference in dimensions) replace connecting rod bolt with new one.
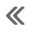 Engine stand setting
Engine stand setting
NOTE:
Explained here is how to disassemble with engine stand supporting transaxle
surface. When using a different
type of engine stand, note difference in steps, etc.
Remove engine and t ...
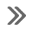 How to select piston and bearing
How to select piston and bearing
DESCRIPTION
Selection points
Selection parts
Selection items
Selection methods
Between cylinder block to
crankshaft
Main bearing
Main bearing grade (bearing
thick ...
Other materials:
Exhaust manifold and three way
catalyst
Exploded View
Cylinder head
Exhaust manifold and three way
catalyst gasket
Exhaust manifold cover (upper)
Exhaust manifold and three way catalyst
Exhaust manifold cover (lower
front)
Exhaust manifold cover (lower rear)
Air fuel ratio (A/F) senso ...
ID registration cannot be completed
Description
The ID of the tire pressure sensor installed in each wheel cannot be
registered in the tire pressure monitoring
system. Inspect the tire pressure sensor or the tire pressure monitoring system
circuit.
Diagnosis Procedure
1.CHECK TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR ACTIVATION TOOL
Check tire pr ...
The light reminder warning does not sound
Description
Light reminder warning does not sound even though headlamp is illuminated.
Diagnosis Procedure
1.CHECK COMBINATION METER INPUT SIGNAL
Select the "Data Monitor" for the "METER/M&A" and check the "BUZZER" monitor
value.
Is the inspection result ...
